Explanation of Common Terms
Database / RDBMS
A relational database (RDB) is a collective set of multiple data sets organized by tables, records and columns. RDBs establish a well-defined relationship between database tables. Tables communicate and share information, which facilitates data searchability, organization and reporting.
RDBs use Structured Query Language (SQL), which is a standard user application that provides an easy programming interface for database interaction.
Table
A table is a named relational database data set that is organized by rows and columns. The relational table is a fundamental relational database concept because tables are the primary form of data storage.
Columns form the table’s structure, and rows form the content. Tables allow restrictions for columns (i.e., allowed column data type) but not rows. Every database table must have a unique name.
Tuple
In the context of relational databases, a tuple is one record (one row). The information in a database can be thought of as a spreadsheet, with columns (known as fields or attributes) representing different categories of information, and tuples (rows) representing all the information from each field associated with a single record.
| Name | Address | Phone |
|---|---|---|
| Steven Diego | 330 S. Sanitary Street, Raleigh, NC 27529 | 919-555-1212 |
Fields / Attributes
The named columns of the database, e.g. “Name”, “Address”, etc. above.
Schema
A database schema is the blueprint of how the database will be laid out, which attributes will be keys or indexes, and for the others, what naming scheme will be employed. It will help ensure that the layout makes sense before you actually start building the database on the server.
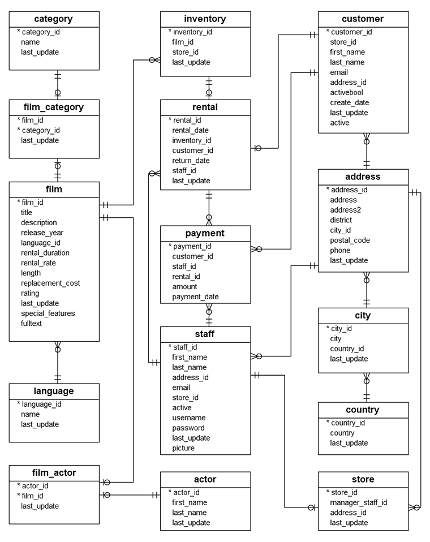
Example Database
This is an ERD (Entity Relationship Diagram) of a simple database.
Back to Class 1 Contents